How does the Fair Credit Billing Act protect consumer credit ratings?
Who does the Fair Credit Billing Act protect
consumers
The Fair Credit Billing Act is a 1974 federal law enacted to protect consumers from unfair credit billing practices. It enables individuals to dispute unauthorized charges on their accounts and those for undelivered goods or services.
How does the Fair Credit Reporting Act regulates credit reports on both consumers and businesses
Key Takeaways. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) governs how credit bureaus can collect and share information about individual consumers. Businesses check credit reports for many purposes, such as deciding whether to make a loan or sell insurance to a consumer. Employers may check them, too.
What are the 3 ways that the Federal Fair Credit Reporting Act of 1970 protects consumers
How does the Fair Credit Reporting Act protect consumersYou must be notified if the information in your credit file was used against you.You have a right to know the information contained in your file.You have a right to request a credit score.You have a right to dispute inaccurate or false information.
What is the Fair Credit Billing Act
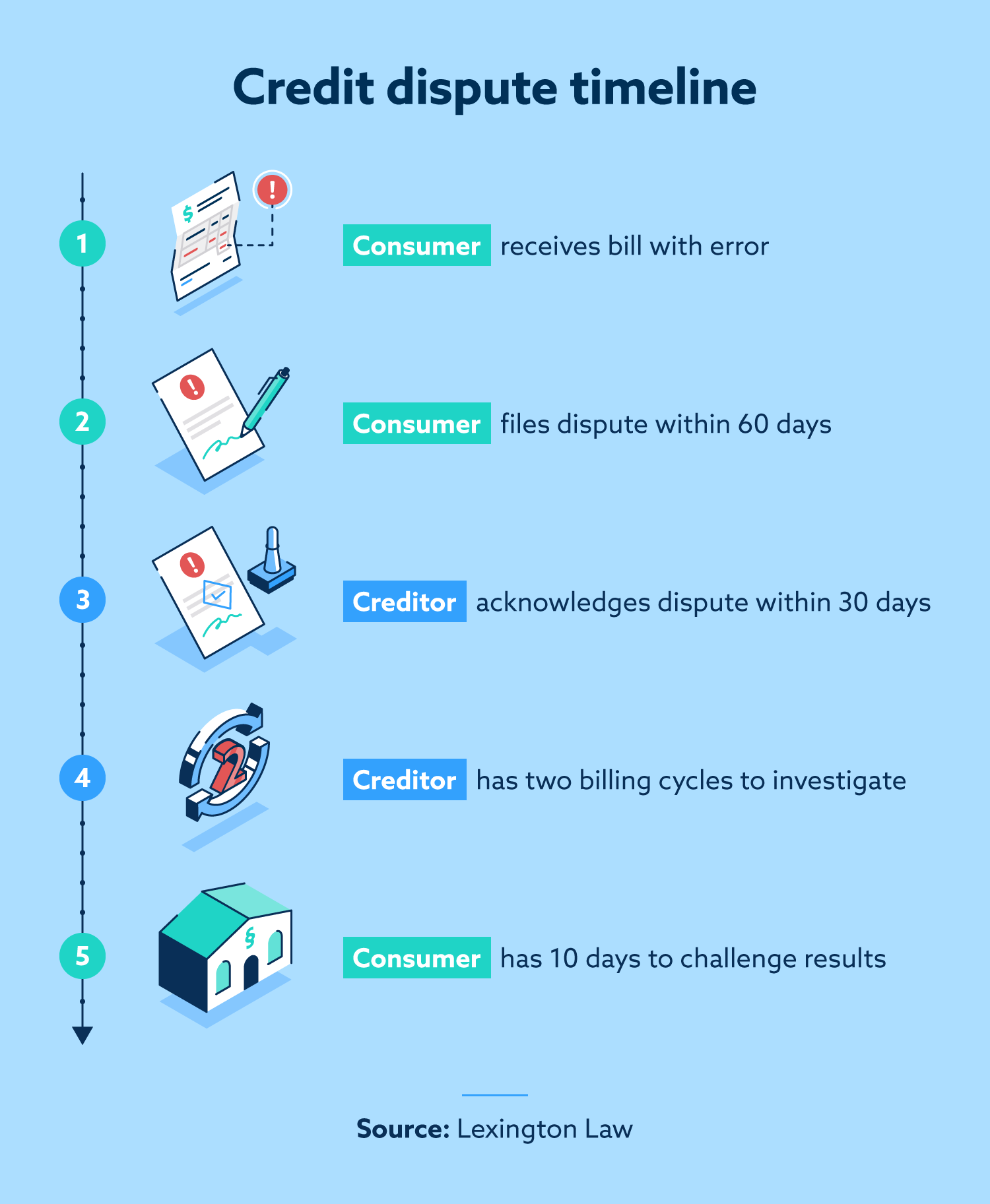
The Act requires creditors to give consumers 60 days to challenge certain disputed charges over $50 such as wrong amounts, inaccurate statements, undelivered or unacceptable goods, and transactions by unauthorized users. Also, the Act limits liability of consumers for transactions by unauthorized users to $50.
What type of accounts does the Fair Credit Billing Act apply to
The FCBA applies only to billing errors on “open-end” accounts, like credit cards and revolving charge accounts. It does not apply to debit card transactions or disputes involving installment contracts with a fixed schedule of payments, like those used to buy cars or furniture.
Who protects the credit rights of consumers
The Bureau of Consumer Protection provides tips and advice about money and credit, homes and mortgages, health and fitness, jobs and making money, and privacy and identity.
How does the Fair Credit Reporting Act help consumers
The FCRA gives you the right to be told if information in your credit file is used against you to deny your application for credit, employment or insurance. The FCRA also gives you the right to request and access all the information a consumer reporting agency has about you (this is called "file disclosure").
What does the Fair Credit Reporting Act give the consumer the right to do quizlet
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is a federal law that requires: Lenders, employers, insurance companies, and anyone using a consumer report to exercise fairness, confidentiality, and accuracy in preparing, submitting, using, and disclosing credit information.
What is the consumer credit Act and how does it protect consumers
The Consumer Credit Act covers a number of different types of consumer credit and related activities. It requires certain credit providers to be licensed. It prescribes requirements in relation to the provision of certain types of credit.
What are 5 laws that protect consumers using credit
The Equal Credit Opportunity Act.The Fair Credit Reporting Act.The Fair Debt Collection Practices Act.The Truth in Lending Act.The Credit Repair Organizations Act.Dealing With Businesses Who Break the Law.
What does the Fair Credit Reporting Act enable consumers to do with their credit
The FCRA gives you the right to be told if information in your credit file is used against you to deny your application for credit, employment or insurance. The FCRA also gives you the right to request and access all the information a consumer reporting agency has about you (this is called "file disclosure").
What are the damages for the Fair Credit Billing Act
If your rights have been violated under the Fair Credit Billing Act, you are entitled to your actual damages, statutory damages up to $5,000, and possibly punitive damages if the creditor has a history of violating other consumers' rights in the same way.
What must be given to consumers under the provisions of the Fair Credit Reporting Act
The FCRA gives you the right to be told if information in your credit file is used against you to deny your application for credit, employment or insurance. The FCRA also gives you the right to request and access all the information a consumer reporting agency has about you (this is called "file disclosure").
What is the Consumer Credit Act and how does it protect consumers
The Consumer Credit Act covers a number of different types of consumer credit and related activities. It requires certain credit providers to be licensed. It prescribes requirements in relation to the provision of certain types of credit.
What are two laws that protect consumers in regard to credit
The Fair Credit Reporting Act regulates credit reports. The Equal Credit Opportunity Act prevents creditors from discriminating against individuals. The Fair Debt Collection Practices Act established rules for debt collectors. The Electronic Fund Transfer Act protects consumer finances during electronic payments.
Does the Fair Credit Reporting Act allow consumers to have access to their credit report
The FCRA also gives you the right to request and access all the information a consumer reporting agency has about you (this is called "file disclosure"). You can get one free file disclosure every 12 months from each national credit bureau by going to AnnualCreditReport.com.
How does the fair and Accurate credit Transaction Act help consumers keep aware of what is on their credit report
It gives consumers the right to one free credit report a year from the credit reporting agencies, and consumers may also purchase, for a reasonable fee, a credit score along with information about how the credit score is calculated.
What is the purpose of the Fair Credit Billing Act quizlet
The FCBA protects consumers against inaccurate or unwarranted charges. Cardholders have protection against liability for fraudulent charges under FCBA if their credit card details have been compromised in a data breach or if they discover a thief has gained access to their credit details.
What do all consumers have the right to according to the Fair Credit Reporting Act
• You have the right to ask for a credit score.
your credit-worthiness based on information from credit bureaus. You may request a credit score from consumer reporting agencies that create scores or distribute scores used in residential real property loans, but you will have to pay for it.
What are the three major rights given to consumers under the Fair Credit Reporting Act
The FCRA gives you the right to be told if information in your credit file is used against you to deny your application for credit, employment or insurance. The FCRA also gives you the right to request and access all the information a consumer reporting agency has about you (this is called "file disclosure").
