How is the sale of common stock recorded if sold above par?
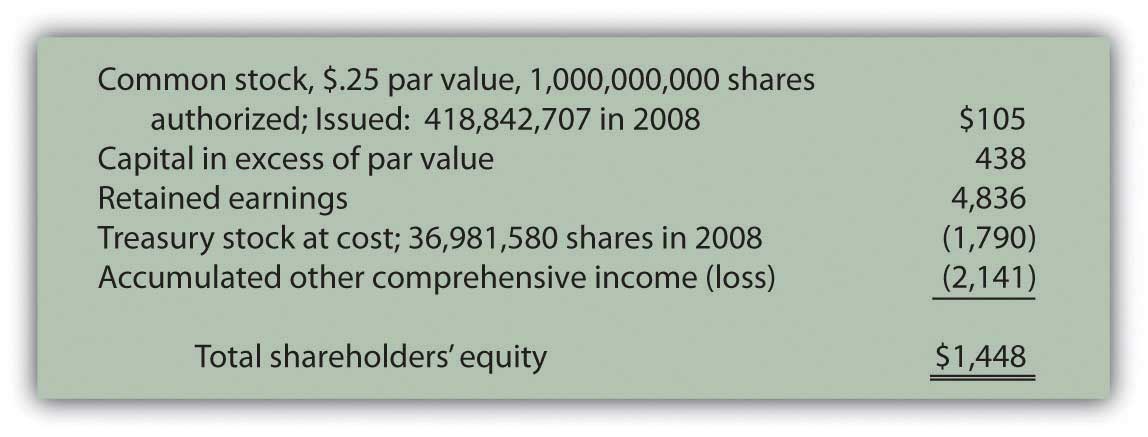
What is this result after common stock is sold for more than its par value
Capital surplus
Capital surplus, or share premium, most commonly refers to the surplus resulting after common stock is sold for more than its par value.
What happens if common stock is issued for an amount greater than par value
The account used for the proceeds greater than par value is called "Additional Paid-In-Capital." The common stock account is credited for the amount of par value received. In this example, the company received proceeds of $100,000 (100,000 shares issued at $1/share par value).
What is the journal entry for issuing common stock above par
If the company sells the shares for more than the par value, then you would credit APIC. IF the company sells the shares for less than the par value, then you would debit APIC. In the example below, the company sold 500 shares for $20 per share.
Cached
What are the steps to record the sale of common stock
Common stock.
When a company such as Big City Dwellers issues 5,000 shares of its $1 par value common stock at par for cash, that means the company will receive $5,000 (5,000 shares × $1 per share). The sale of the stock is recorded by increasing (debiting) cash and increasing (crediting) common stock by $5,000.
CachedSimilar
What happens when a bond is selling for more than its par value
If a bond is trading at a premium, this simply means it is selling for more than its face value.
Is common stock sold at par value
Par value is the value of a single common share as set by a corporation's charter. It is not typically related to the actual value of the shares. In fact it is often lower. Any stock certificate issued for shares purchased shows the par value.
Do you record common stock at par value
Upon issuance, common stock is recorded at par value with any amount received above that figure reported in an account such as capital in excess of par value. If issued for an asset or service instead of cash, the recording is based on the fair value of the shares given up.
When a corporation issues shares of common stock for an amount above par
When common stock has a designated par value, and common stock is issued at an amount above par, which entry is recorded Credit common stock for the par amount. A company that repurchases its own securities accounts for the buyback as: Retired shares or treasury shares.
How to record issuance of common stock with no par value
The accounting entry for a no-par-value stock will be a debit to the cash account and credit to the common stock account within shareholder's equity.
What is the journal entry for par stock
Stock issuances
| Debit | Cash or other item received | (shares issued x price paid per share) or market value of item received |
|---|---|---|
| Credit | Common (or Preferred) Stock | (shares issued x PAR value) |
| Credit | Paid in capital in excess of par value, common (or preferred) stock | (difference between value received and par value of stock) |
What is the journal entry for common stock par value
Common shares with par value are journalized by debiting cash (asset) for the amount received for the shares and crediting common shares (equity) up to the par value, with the balance of the entry credited to additional paid-in capital (equity).
What happens when common stock is sold
Companies sell common stock to raise money, which they then use for various initiatives, like general corporate purposes, growth or new products. Investors who buy common stock own a small piece of the company and share in its profits. They usually have the right to vote on what happens at the company.
When a bond trades above par the current yield is
If the bond trades at par value, the current yield and coupon rate are the same. In contrast, if the bond trades above its par value (premium), the current yield is less than the coupon rate.
Can a bond be issued for a price above its par value
premium
Are Bonds Issued at Par Value Bonds are not necessarily issued at their par value. They could also be issued at a premium or a discount depending on the level of interest rates in the economy. A bond that is trading above par is said to be trading at a premium, while a bond trading below par is trading at a discount.
How does par value relate to common stock
Par value is the value of a single common share as set by a corporation's charter. It is not typically related to the actual value of the shares. In fact it is often lower. Any stock certificate issued for shares purchased shows the par value.
How do you record common stock with no par value
If a firm issues stocks with no par value, the cash account is debited, and either the ordinary shares account or the capital share account is credited.
How do you record sale of par value stock and no par stock
The accounting entry will be a debit to cash, a credit to the common stock account, and a credit paid-in capital for the excess of par value amount. If a company has sold no-par-value stocks, the proceeds from the transaction will be credited to the common stock account only.
What happens when a company issues more common stock
When companies issue additional shares, it increases the number of common stock being traded in the stock market. For existing investors, too many shares being issued can lead to share dilution. Share dilution occurs because the additional shares reduce the value of the existing shares for investors.
What is excess over par of shares issued
When a company issues shares of stock to raise capital, it is common for the shares to be sold at a price higher than the par value. The difference between the actual price at which the shares are sold and the par value of the shares is recorded as Capital in Excess of Par.
How do you record par value stock
On the balance sheet, the par value of outstanding shares is recorded to common stock, and the excess (that is, the amount the market price adds to par value) is recorded to additional paid-in capital. The sum of common stock and additional paid-in capital represents the paid-in capital.
