Is bad debts debit or credit in trial balance?
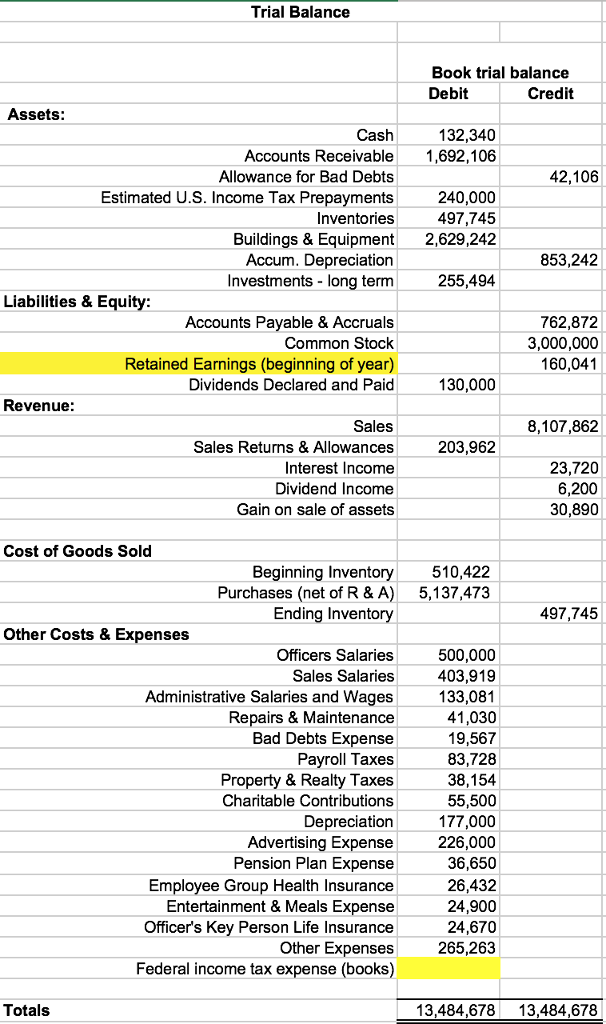
Is bad debt a debit or credit in trial balance
Bad Debts is shown on the debit side of profit or loss account.
Where does bad debt go on trial balance
Irrecoverable debts are also referred to as 'bad debts' and an adjustment to two figures is needed. The amount goes into the statement of profit or loss as an expense and is deducted from the receivables figure in the statement of financial position.
Is bad debts a debit
Recording bad debt involves a debit and a credit entry. Here's how it's done: A debit entry is made to a bad debt expense. An offsetting credit entry is made to a contra asset account, which is also referred to as the allowance for doubtful accounts.
Why is bad debt expense a debit
When sales transactions are recorded, a related amount of bad debt expense is also recorded, on the theory that the approximate amount of bad debt can be determined based on historical outcomes. This is recorded as a debit to the bad debt expense account and a credit to the allowance for doubtful accounts.
What comes in debit side of trial balance
All the assets must be recorded on the debit side. All the liabilities must be recorded on the credit side. All incomes or gains must be recorded on the credit side. All the expenses must be recorded on the debit side.
How do you treat bad debt written off in a trial balance
Since bad debts are written off at the time of occurrence during the accounting period, bad debts account appears inside the trial balance. In such case, all that is to be done is to transfer bad debts account to the debit side of Profit and Loss Account.
What type of account is bad debts
Bad debt is a type of account receivable for an organisation that has become uncollectible from the customer due to the customer's inability to pay the amount of money taken on credit from the organisation.
Is bad debt an expense
Accountants record bad debt as an expense under Sales, General, and Administrative expenses (SG&A) on the income statement.
What type of account is bad debt expense
Bad debt expense or BDE is an accounting entry that lists the dollar amount of receivables your company does not expect to collect. It reduces the receivables on your balance sheet. Accountants record bad debt as an expense under Sales, General, and Administrative expenses (SG&A) on the income statement.
What goes in debit and credit in trial balance
When looking at the trial balance meaning, it's helpful to define what would go into each side of the equation. Debit balances include asset and expense accounts. Credit balances include liabilities, capital, and income accounts.
Which item shows a credit balance in the trial balance
Expenses and assets are accounted for as debit balances, while income and liabilities are considered credit balances.
How do you record bad debt
To record the bad debt expenses, you must debit bad debt expense and a credit allowance for doubtful accounts. With the write-off method, there is no contra asset account to record bad debt expenses. Therefore, the entire balance in accounts receivable will be reported as a current asset on the balance sheet.
How do you record bad debts written off on a balance sheet
The entry to write off the bad account under the direct write-off method is:Debit Bad Debts Expense (to report the amount of the loss on the company's income statement)Credit Accounts Receivable (to remove the amount that will not be collected)
How do you record bad debt in accounting
To record the bad debt entry in your books, debit your Bad Debts Expense account and credit your Accounts Receivable account. To record the bad debt recovery transaction, debit your Accounts Receivable account and credit your Bad Debts Expense account. Next, record the bad debt recovery transaction as income.
Is bad debt account an asset or liability
Is bad debt included in assets or liabilities Bad debt is basically an expense for the company, recorded under the heading of sales and general administrative expenses. But the bad debt provision account is recorded as a contra-asset on the balance sheet.
How do you account for bad debts
The double entry for a bad debt will be:
We debit the bad debt expense account, we don't debit sales to remove the sale. The sale was still made but we need to show the expense of not getting paid. We then credit trade receivables to remove the asset of someone owing us money.
What type of account is a bad debt
Bad debt is a type of account receivable for an organisation that has become uncollectible from the customer due to the customer's inability to pay the amount of money taken on credit from the organisation.
How do you record bad debts
Bad debt is debt that cannot be collected. It is a part of operating a business if that company allows customers to use credit for purchases. Bad debt is accounted for by crediting a contra asset account and debiting a bad expense account, which reduces the accounts receivable.
Is bad debt an asset or expense
expense
Bad debt is considered an expense which offsets assets in business's accounts receivable, also known as the net realizable value of the accounts receivable. The expense is recorded according to the matching principle so that accounts receivable assets are not overstated.
What should be debited in trial balance
The rules for preparing a trial balance are as follows: All the assets must be recorded on the debit side. All the liabilities must be recorded on the credit side. All incomes or gains must be recorded on the credit side.
