Is DoorDash pay reported to IRS?
Will the IRS know if I work for DoorDash
An audit means that the IRS will review your financial records to make sure that income is reported correctly and that it matches what you've submitted on your tax return. You will likely receive Form 1099-NEC from Grubhub, Postmates, and DoorDash if you earn more than $600 during the calendar year.
Cached
Does DoorDash report wages to IRS
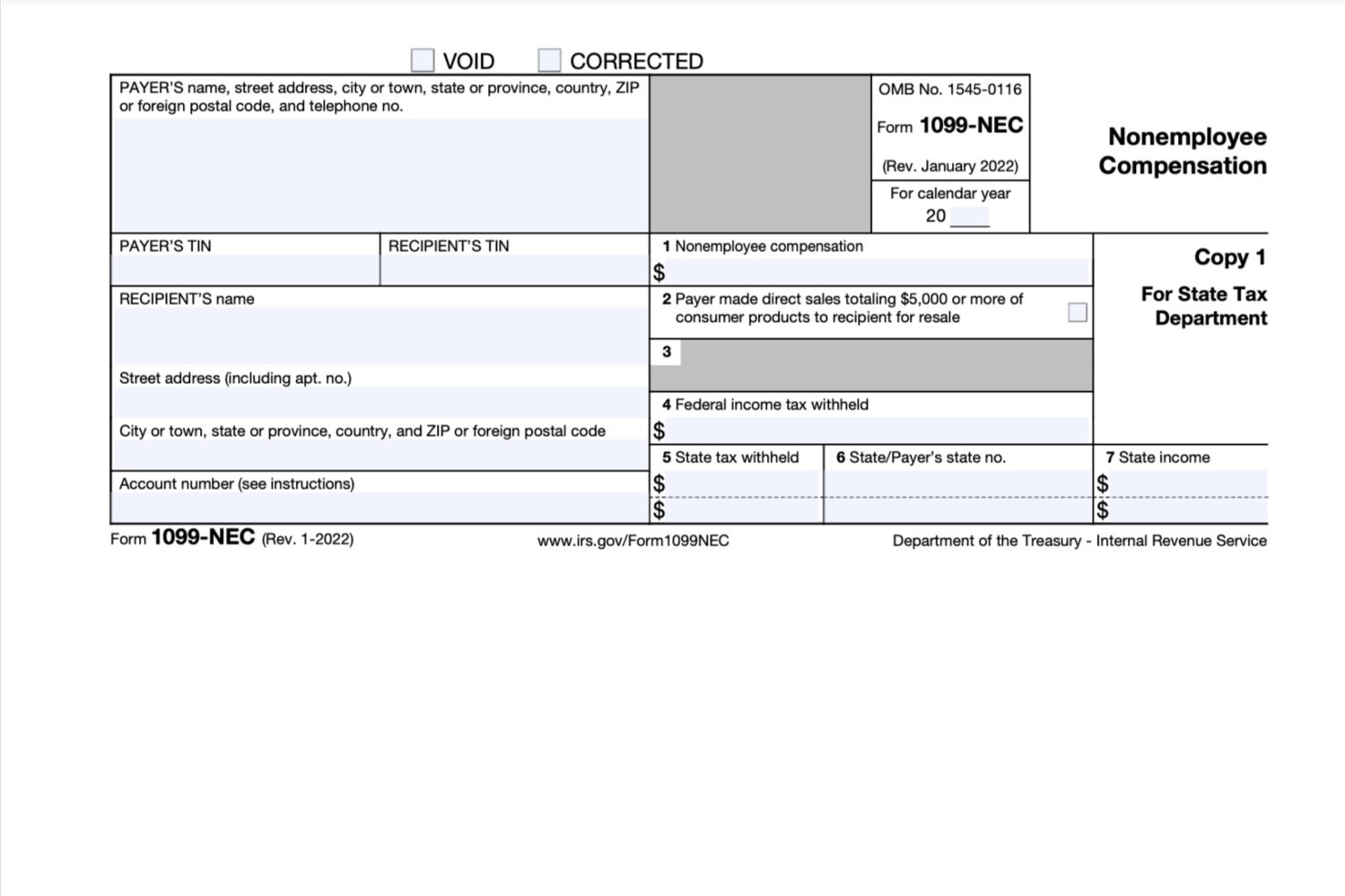
A 1099-NEC form summarizes Dashers' earnings as independent contractors in the US. It's provided to you and the IRS, as well as some US states, if you earn $600 or more in 2023. If you're a Dasher, you'll need this form to file your taxes.
Cached
Do I have to pay taxes if I did DoorDash
Doordash is considered self-employment, which means you'll pay taxes using 1099 forms. It also means you're able to write off business expenses that could help you save on your tax bill.
Cached
Does DoorDash send 1099 to IRS
Your 1099 tax form will be mailed to you, if you don't receive an email from Stripe or don't consent to e-delivery. Please allow up to 10 business days for mail delivery. DoorDash will file your 1099 tax form with the IRS and relevant state tax authorities.
Cached
How much can you make on DoorDash without paying taxes 2023
Yes – Just like everyone else, you'll need to pay taxes. If you earned more than $600 while working for DoorDash, you are required to pay taxes. It doesn't apply only to DoorDash employees. To compensate for lost income, you may have taken on some side jobs.
How much can you make on the side without paying taxes
If you made a net profit of $400 or more from your side hustle, you have to pay taxes on it, according to the IRS. “Any earned income is subject to taxes and when you work for yourself or are a 1099 worker, there are no taxes withheld so you will be responsible for saving for any taxes due,” O'Leary says.
What happens if you don’t pay DoorDash taxes
If you cannot pay the full amount, you will face penalties and owe interest. Another option is to pay quarterly estimated payments direct to the IRS. This could help you avoid a surprise tax bill and possibly keep you from paying any penalties.
Do I have to file taxes for DoorDash if I made less than $600
Yes. You have to file taxes and report all income you receive as an independent contractor, even if it's less than $600 and you don't get a 1099 form. Does DoorDash report to the IRS DoorDash will report the income of all its DoorDashers who earn more than $600 to the IRS.
How do I avoid paying taxes on DoorDash
9 Best Tax Deductions for Doordash Drivers in 2023Mileage or car expenses.Phone & Service Bills.Hot bags, blankets & Courier backpacks.Tolls.Parking.Inspections.Roadside Assistance.Health Insurance.
How does the IRS know if you have a side hustle
You report self-employment income on Schedule C, which flows to Form 1040. If you make more than $20,000 or 200 transactions using a third-party payment app like Venmo or PayPal, you may get a Form 1099-K from them. A new rule which goes into effect next year means a transaction of $600 or more could trigger the form.
What happens if you don’t report side income
Failure to report earned income is a form of tax fraud. If you don't report income on your side gig and you are audited (even several years later), you could incur a failure-to-pay penalty, Hearn says. That penalty equals 0.5 percent of your unpaid taxes for each month, or part of a month, after your tax return is due.
How much can you make on DoorDash before having to file taxes
$600
DoorDash & 1099s
Each year, tax season kicks off with tax forms that show all the important information from the previous year. You'll receive a 1099-NEC if you've earned at least $600 through dashing in the previous year. Form 1099-NEC reports income you received directly from DoorDash (ex.
How does the IRS find out about unreported income
The IRS receives information from third parties, such as employers and financial institutions. Using an automated system, the Automated Underreporter (AUR) function compares the information reported by third parties to the information reported on your return to identify potential discrepancies.
How much money can you make without reporting to IRS
Tax Year 2023 Filing Thresholds by Filing Status
| Filing Status | Taxpayer age at the end of 2023 | A taxpayer must file a return if their gross income was at least: |
|---|---|---|
| single | under 65 | $12,950 |
| single | 65 or older | $14,700 |
| head of household | under 65 | $19,400 |
| head of household | 65 or older | $21,150 |
Can you go to jail for not reporting income to IRS
Tax evasion in California is punishable by up to one year in county jail or state prison, as well as fines of up to $20,000. The state can also require you to pay your back taxes, and it will place a lien on your property as a security until you pay taxes.
What are red flags for the IRS
Some red flags for an audit are round numbers, missing income, excessive deductions or credits, unreported income and refundable tax credits. The best defense is proper documentation and receipts, tax experts say.
Do I have to report income less than $100
Why is it necessary to report all income While the Internal Revenue Service will require clients and businesses to issue the 1099 form when the payments they make for the tax year are over $600, there is no such requirement for reporting income.
Do I have to file taxes if I made less than $15 000
Do I Need to File Taxes Not everyone is required to file or pay taxes. Depending on your age, filing status, and dependents, for the 2023 tax year, the gross income threshold for filing taxes is between $12,550 and $28,500.
How does the IRS figure out about unreported income
The IRS receives information from third parties, such as employers and financial institutions. Using an automated system, the Automated Underreporter (AUR) function compares the information reported by third parties to the information reported on your return to identify potential discrepancies.
How do you tell if IRS is investigating you
Signs that the IRS might be investigating youAbrupt change in IRS agent behavior.Disappearance of the IRS auditor.Bank records being summoned or subpoenaed.Accountant contacted by CID or subpoenaed.Selection of a previous tax return for audit.
