What does the Fair Credit Billing Act FCBA do?
Who does the Fair Credit Billing Act protect
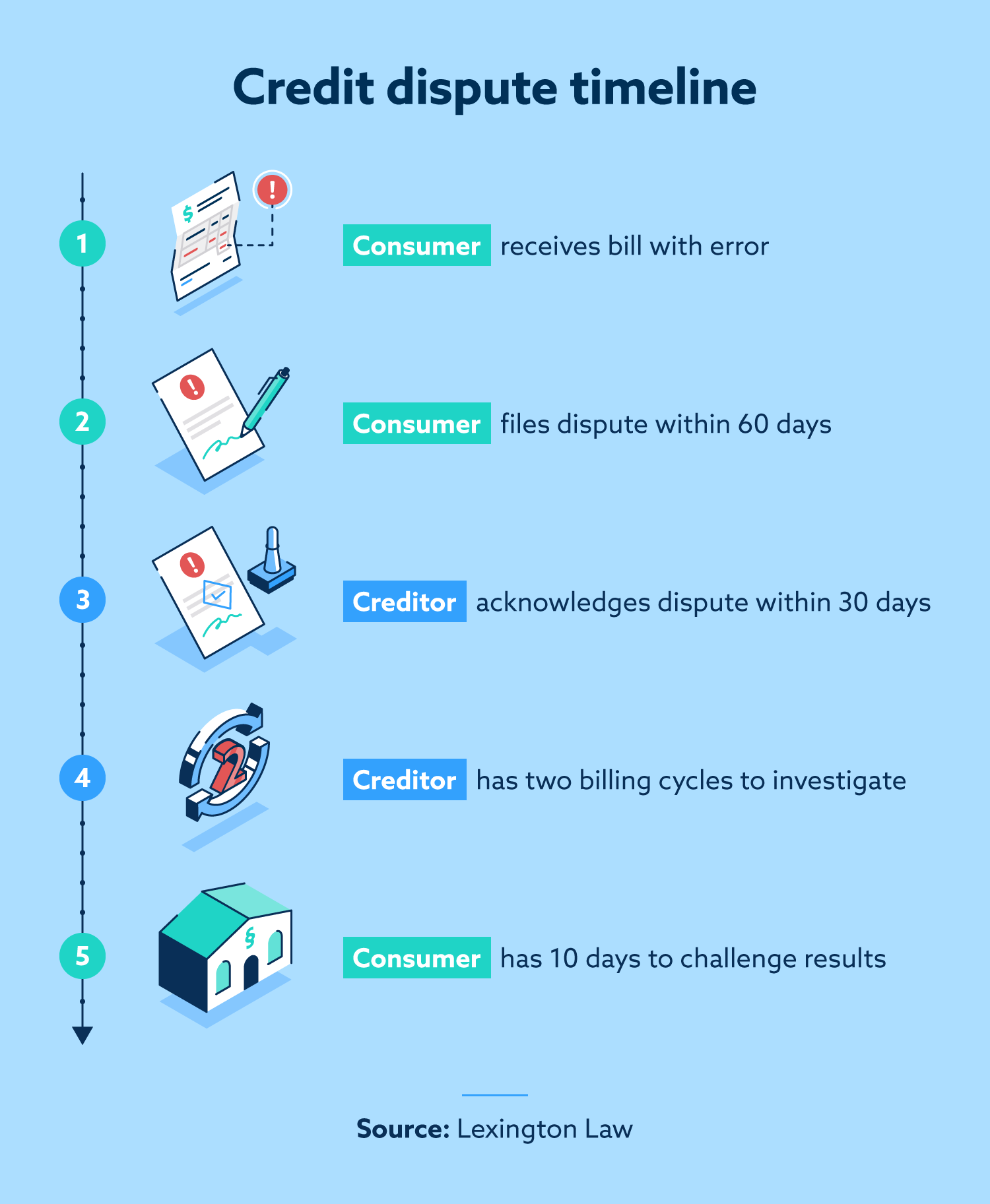
consumers
The Fair Credit Billing Act is a 1974 federal law enacted to protect consumers from unfair credit billing practices. It enables individuals to dispute unauthorized charges on their accounts and those for undelivered goods or services.
Cached
Which type of accounts does the Fair Credit Billing Act FCBA apply to
The FCBA applies only to billing errors on “open-end” accounts, like credit cards and revolving charge accounts.
Cached
What is the purpose of the Fair Credit Billing Act and the electronic fund
The Fair Credit Billing Act (FCBA) and Electronic Fund Transfer Act (EFTA) establish procedures for resolving mistakes on credit billing and electronic fund transfer account statements, including: Charges or electronic fund transfers that you – or anyone you have authorized to use your account – have not made.
Cached
What is the Fair Credit Billing Act quizlet
The FCBA protects consumers against inaccurate or unwarranted charges. Cardholders have protection against liability for fraudulent charges under FCBA if their credit card details have been compromised in a data breach or if they discover a thief has gained access to their credit details.
What are the rights of the FCBA
The Act requires creditors to give consumers 60 days to challenge certain disputed charges over $50 such as wrong amounts, inaccurate statements, undelivered or unacceptable goods, and transactions by unauthorized users. Also, the Act limits liability of consumers for transactions by unauthorized users to $50.
What is the private right of action of the FCBA
That is, failure of a financial institution to adhere to these provisions gives a consumer the ability to bring a private action against the creditor. The FCBA allows for actual damages, statutory damages of twice the finance charges, court costs, and attorneys fees.
What is required under the Fair Credit Reporting Act
The FCRA specifies those with a valid need for access. reporting agency may not give out information about you to your employer, or a potential employer, without your written consent given to the employer. Written consent generally is not required in the trucking industry.
What is the purpose of the Fair Credit Billing Act and the Electronic Fund Transfer Act quizlet
In the case of an error in credit billing or electronic fund transfer, these acts protect the consumer by following established procedures in resolving mistakes. Ensures debt collectors follow specific procedures and protocols when collecting debts and protects against deceptive, abusive or unfair collection practices.
What was the Fair Credit Reporting Act FCRA intended to responses
It was enacted in 1970 to ensure fairness, accuracy and privacy of the personal information contained in the files of the credit reporting agencies.
What are the three major rights given to consumers under the Fair Credit Reporting Act
The FCRA gives you the right to be told if information in your credit file is used against you to deny your application for credit, employment or insurance. The FCRA also gives you the right to request and access all the information a consumer reporting agency has about you (this is called "file disclosure").
What happens if Fair Credit Billing Act is violated
Even if the billing turns out to be correct, they still cannot collect the disputed billing amount. When the rights of the consumers provided under the FCBA act are violated, he/she can file a lawsuit against the creditor.
What is an example of the Fair Credit Reporting Act
For example, employers can request a job applicant's credit report, but only with the applicant's permission. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) mandates that when a business pulls a credit report on someone, they must specify the reason, such as: In conjunction with a loan request. For employment purposes.
What are the major provisions of the Fair Credit Billing Act quizlet
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is a federal law that requires: Lenders, employers, insurance companies, and anyone using a consumer report to exercise fairness, confidentiality, and accuracy in preparing, submitting, using, and disclosing credit information.
What is the primary objective of the Electronic Fund Transfer Act EFTA
The Electronic Fund Transfer Act (EFTA) (15 U.S.C. 1693 et seq.) of 1978 is intended to protect individual consumers engaging in electronic fund transfers (EFTs) and remittance transfers.
What are the most common FCRA violations
Some of the common violations include:Furnishing and Reporting Old Information.Mixing Files.Debt Dispute Procedures for Credit Bureaus.Debt Dispute Violations for Creditors.Privacy Violations.Withholding Notices.Willful FCRA Violations.Negligent FCRA Violations.
What is the purpose of the Notice to consumers required by the Fair Credit Reporting Act
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), 15 U.S.C. 1681-1681y, requires that this notice be provided to inform users of consumer reports of their legal obligations. State law may impose additional requirements.
What is a violation of the Fair Credit Reporting Act
Common violations of the FCRA include:
Creditors give reporting agencies inaccurate financial information about you. Reporting agencies mixing up one person's information with another's because of similar (or same) name or social security number. Agencies fail to follow guidelines for handling disputes.
What are common violations of the FCRA
Most Frequent Violations of the Fair Credit Reporting ActReporting outdated information.Reporting false information.Accidentally mixing your files with another consumer.Failure to notify a creditor about a debt dispute.Failure to correct false information.
What is an example of a violation of the Fair Credit Reporting Act
Common violations of the FCRA include:
Failure to update reports after completion of bankruptcy is just one example. Agencies might also report old debts as new and report a financial account as active when it was closed by the consumer. Creditors give reporting agencies inaccurate financial information about you.
What does the law require under the Fair Credit Reporting Act
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) mandates that when a business pulls a credit report on someone, they must specify the reason, such as: In conjunction with a loan request. For employment purposes. As part of a credit check by a landlord.
