What is bank rate rate?
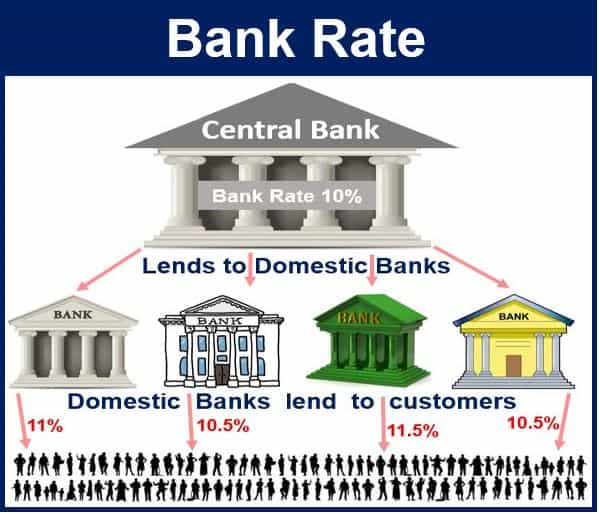
What is bank rate vs rate of interest
Bank rate directly affects the rates of interest (ROI) of commercial bank loans. Commercial banks eventually charge their customers when there is an increase in the bank rate. It is to compensate for the higher interest they pay to RBI. The bank rate is also meant for a long-term rate change and economic impact.
What is bank rate how it works
What is a Bank Rate Bank rate is a rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) provides the loan to commercial banks without keeping any security. There is no agreement on repurchase that will be drawn up or agreed upon with no collateral as well. The RBI allows short-term loans with the presence of collateral.
Is bank rate the same as cash rate
While the cash rate does not determine interest rates directly, banks and lenders will pay close attention to it when setting them, and will often respond to moves that the RBA makes. If the RBA raises the cash rate, then it will cost more for banks to transfer money between themselves.
What is the difference between bank rate and lending rate
Simply put, repo rate is the rate at which the RBI lends to commercial banks by purchasing securities while bank rate is the lending rate at which commercial banks can borrow from the RBI without providing any security.
Why are bank interest rates so high
The interest rate on your savings account is influenced by what the Federal Reserve does. The Federal Reserve has been raising the federal funds rate to combat inflation. When the Federal Reserve raises rates, the interest rate on your savings account tends to go up, too.
What are the 2 different types of interest rates
When borrowing money with a credit card, loan, or mortgage, there are two interest rate types: Fixed Rate Interest and Variable Rate Interest.
What happens when bank rate rises
For example, raising rates can help ease inflation: A higher federal funds rate generally leads to higher rates for loans or credit cards, so households may be less willing to borrow money. That could lead to less spending, which could result in lower prices and less inflation.
How do you calculate bank rate
A = P(1 + R/N) NTA: the amount of money you'll have in your bank account after interest is paid.P: your principal deposit, or the original balance of your account.R: the yearly interest rate of your account in decimal format (APY)N: the number of times your bank compounds interest in a year (12 times)
What is the cash rate now
The current cash rate is 4.10%. What's on this page: RBA Cash Rate history. Cash Rate & home loan rates.
What is the US cash rate
United States Policy Rate
United States cash rate (Policy Rate: Month End: Effective Federal Funds Rate) was set at 4.83 % pa in Apr 2023, compared with 4.83 % pa in the previous Mar 2023. US Policy Rate averaged 4.13 % pa and is updated monthly, available from Jul 1954 to Apr 2023.
Which bank interest rate is better
Among scheduled private sector banks, Bandhan Bank and DCB Bank offer the best FD interest rates of up to 8.00% p.a. Among scheduled public sector banks, the highest FD rate is offered by the Punjab & Sind Bank of up to 7.35% p.a. for a tenure of 555 days.
Why does bank rate affect interest rates
The Bank Rate sets the amount of interest paid to commercial banks, which in turn influences the rates they charge customers for borrowing, or pay them for saving. If the Bank Rate increases: Unless your interest rates are fixed, the cost of borrowing will go up. Interest earned from savings will increase.
How high will interest rates go in 2023
Since the start of 2023, the Fed has hiked rates 10 times to combat rising inflation. As of May 2023, the federal funds rate ranges from 5.00% to 5.25%. If this prediction is correct, it won't be surprising to see some of the best high-yield savings accounts offering rates exceeding 4%.
Why are bank interest rates so terrible
One reason savings account rates are so low is that financial institutions profit when the rate on the money they lend out is higher than the rate they pay people who deposit money into savings. When rates on loans are low, banks like to keep savings account rates even lower to continue making money on them.
Which type of interest rate is best
#1 – Fixed Interest Rate
This is much easier, and calculations are not at all complex. It gives a clear understanding to the lender and the borrower what the exact amount of interest rate obligation is associated with the loan. Fixed interest is a rate that does not fluctuate with time or during the loan period.
What is an example of a bank interest rate
For example, if the simple interest rate is 5% on a loan of $1,000 for a duration of 4 years, the total simple interest will come out to be: 5% x $1,000 x 4 = $200.
Who gets the money when interest rates rise
“The winners tend to be people who have high savings, and obviously benefit from high interest rates,” Oliver says. “The losers tend to be those with net debt. Those with more net debt tend to suffer because they pay more on interest rates servicing that debt.
Who benefits from higher interest rates
There are some upsides to rising rates: More interest for savers. Banks typically increase the amount of interest they pay on deposits over time when the Federal Reserve raises interest rates. Fixed income securities tend to offer higher rates of interest as well.
What is 6% interest on a $30000 loan
For example, the interest on a $30,000, 36-month loan at 6% is $2,856.
What is an example of bank rate
For example, if the bank rate is 0.75%, banks are likely to charge their customers relatively low-interest rates. In contrast, if the discount rate is 12% or a similarly high rate, banks are going to charge borrowers comparatively higher interest rates.
