What is the correct order of accounting?
What are the 4 phases of accounting in order
The four phases of accounting are as follows:Recording transactions.Classifying transactions.Summarising.Interpreting financial data.
What are the 5 stages of accounting
Defining the accounting cycle with steps: (1) Financial transactions, (2) Journal entries, (3) Posting to the Ledger, (4) Trial Balance Period, and (5) Reporting Period with Financial Reporting and Auditing.
CachedSimilar
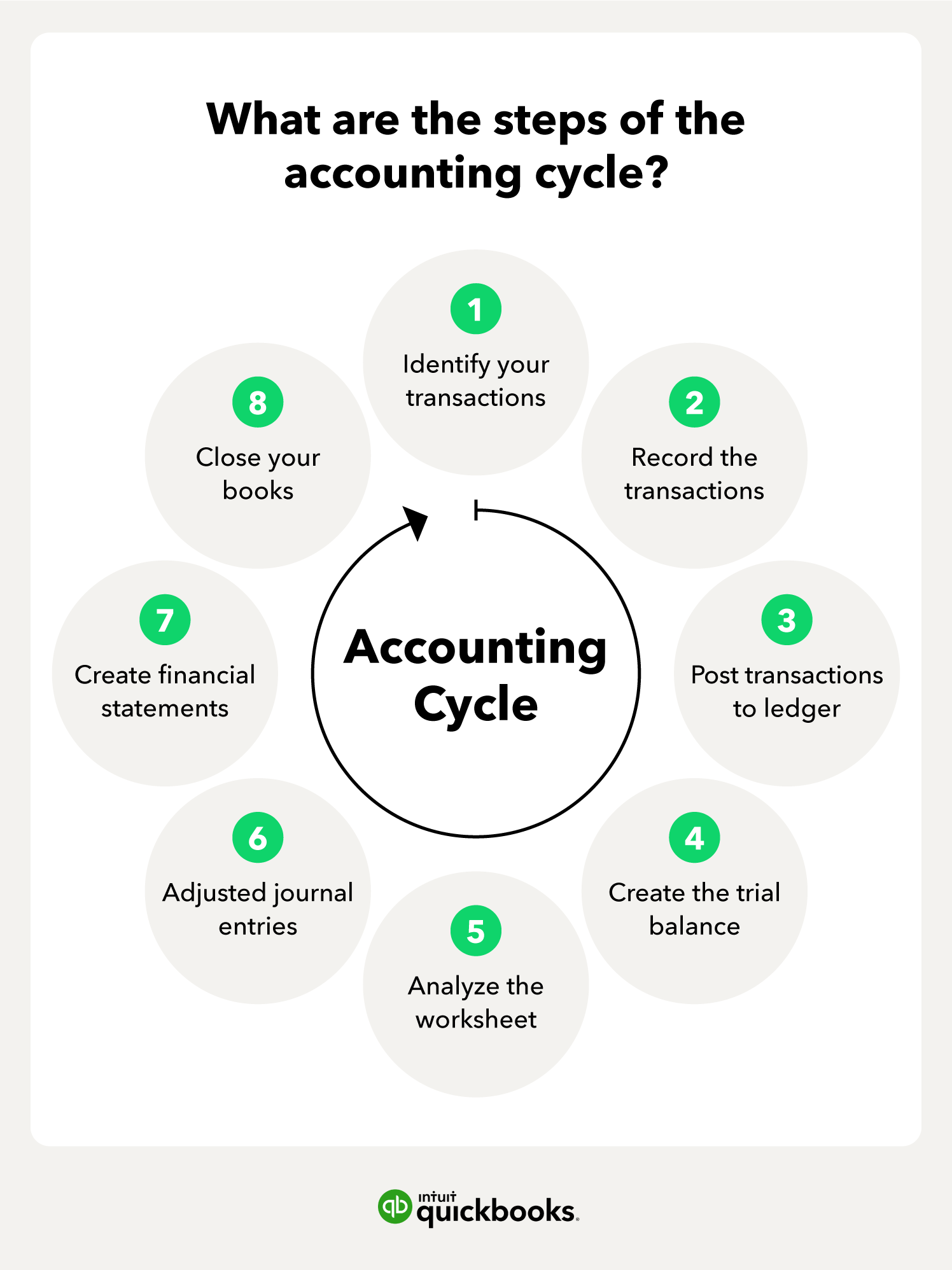
What are the 7 steps in the accounting cycle
The seven steps in the accounting cycle are as follows:Identifying and Analysing Business Transactions.Posting Transactions in Journals.Posting from Journal to Ledger.Recording adjusting entries.Preparing the adjusted trial balance.Preparing financial statements.Post-Closing Trial Balance.
What is the correct sequence for the closing accounting process
The basic sequence of closing entries is as follows: Debit all revenue accounts and credit the income summary account, thereby clearing out the balances in the revenue accounts. Credit all expense accounts and debit the income summary account, thereby clearing out the balances in all expense accounts.
What is the accounting process
What is the Accounting Process Accounting is a process that helps in recording the financial transactions which are necessary for the business. This process includes summarizing, analyzing and reporting the transactions to give an overview to the agencies, regulators and tax collection entities.
What are the four 4 principles of accounting and financial systems
There are four basic principles of financial accounting measurement: (1) objectivity, (2) matching, (3) revenue recognition, and (4) consistency. 3. A special method, called the equity method, is used to value certain long-term equity investments on the balance sheet.
What is accounting standard 5
Accounting Standard 5 (AS 5) deals with the classification and disclosure of specific items in the Statement of Profit and Loss. The purpose of AS 5 is to suggest such a classification and disclosure in order to bring uniformity in the preparation and presentation of statement of net profit or loss across enterprises.
What are the 5 elements of financial accounting
The elements of the financial statements will be assets, liabilities, net assets/equity, revenues and expenses. It is noted in Study 1 that moving along the spectrum from cash to accrual accounting does not mean a loss of the cash based information which can still be generated from an accrual accounting system.
What are the 6 phases of accounting
6 Important Steps in Full Accounting CycleStep 1: Identify the Transaction.Step 2: Record Transactions in a Journal.Step 3: Post to the General Ledger.Step 4: Create a Trial Balance.Step 5: Create Financial Statements.Step 6: Closing the Books.
What are the 6 steps in the accounting process
The six steps of accounting are:Identify and post the transactions.Post transactions to the ledger after passing it through the journal.Determine an unadjusted trial balance for the current period.Record any adjusting entries at the end of the period.Arrange an adjusted trial balance.
What are the 4 financial statements in order
For-profit businesses use four primary types of financial statement: the balance sheet, the income statement, the statement of cash flow, and the statement of retained earnings.
What is the order of accounts on a balance sheet
Order of liquidity is the presentation of assets in the balance sheet in the order of the amount of time it would usually take to convert them into cash. Thus, cash is always presented first, followed by marketable securities, then accounts receivable, then inventory, and then fixed assets. Goodwill is listed last.
What are the 3 important steps in accounting process
Three fundamental steps in accounting are:Identifying and analyzing the business transactions.Recording of the business transactions.Classifying and summarising their effect and communicating the same to the interested users of business information.
What is the basic accounting model
The equation is as follows: Assets = Liabilities + Shareholder's Equity This equation sets the foundation of double-entry accounting, also known as double-entry bookkeeping, and highlights the structure of the balance sheet.
What are the 4 components of accounting
Components of Basic AccountingRecording. The primary function of accounting is to make records of all transactions that the firm enters into.Summarising. Recording of transactions creates raw data.Reporting. Management is answerable to the investors about the company's state of affairs.Analyzing.
What are the 4 accounting standards
Specific examples of accounting standards include revenue recognition, asset classification, allowable methods for depreciation, what is considered depreciable, lease classifications, and outstanding share measurement.
What is accounting standard 7
Accounting Standard 7 (AS 7) relates with accounting of construction contracts. The very purpose of this accounting standard is to specify the accounting treatment of revenue and costs associated with construction contracts.
What is accounting standard 6
AS-6 deals with depreciation of the tangible asset. Hence, only the historical cost, accumulated depreciation on the asset and total depreciation for the period for each class of asset will be recorded. Depreciable value of asset is not to be disclosed according to AS-6.
What are the 4 major elements of financial accounting
These are the Balance Sheet, the Profit and Loss Account, the Cash Flow Statement, and the Statement of Changes in Equity. The article works through a firm's Annual Report, teaches you how to read each of the four financial statements, explains the interdependence between them, and lists common users.
What are the 6 elements of accounting
The accounting elements are Assets, Liabilities, Owners Equity, Capital Introduced, Drawings, Revenue and Expenses. Each account we have is one of these elements. On early task you must master is to be able to allocate each account to its accounting element.
