Why do realtors prefer conventional over FHA?
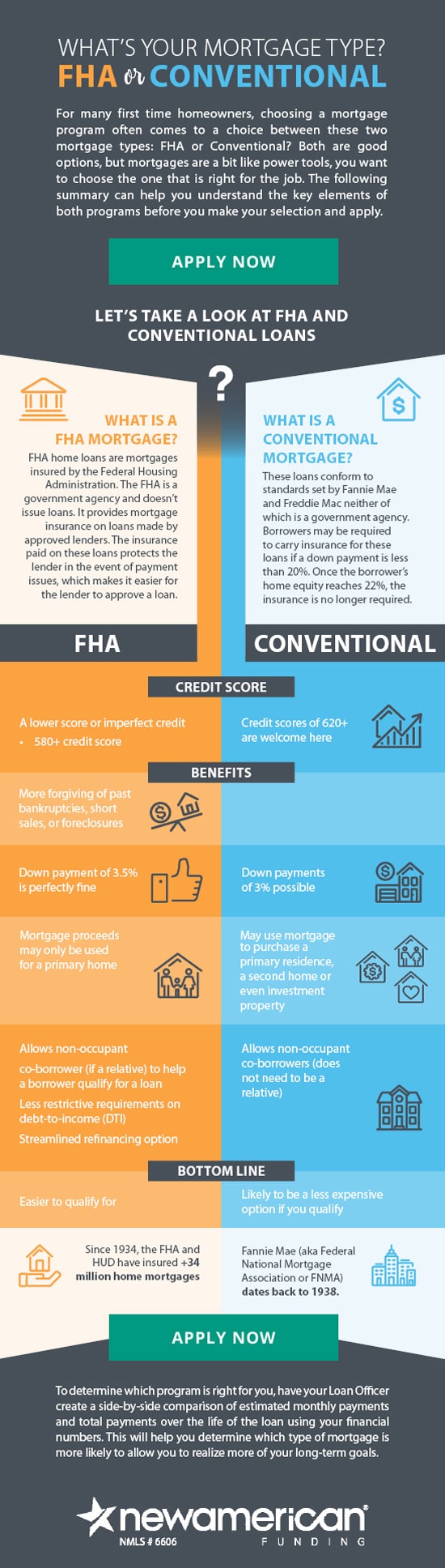
Why do sellers avoid FHA
FHA Underwriting Worries Some Sellers
Because FHA loans help low- to moderate-income borrowers with less-than-stellar credit become homeowners, sellers may feel that FHA buyers are less likely to be approved for a loan than conventional borrowers.
Cached
Is it better to sell to a FHA or conventional loan
"Conventional loans have higher minimum requirements than FHA and require a larger down payment," Yates said. "Sellers prefer a buyer with conventional financing over FHA financing because they feel the buyer is in a better financial position."
Cached
What is the advantage of a conventional loan over an FHA loan
FHA loans allow lower credit scores and are easier to qualify for. Conventional loans allow lower down payments. Hal M. Bundrick is a personal finance writer and a NerdWallet authority in money matters.
Cached
Why do lenders prefer conventional loans
This type of loan uses lower interest rates and less strict credit score requirements. Conventional loans are not backed by a government agency and often use conforming loan limits.
What are the downsides of FHA
Here are some FHA home loan disadvantages: An extra cost – an upfront mortgage insurance premium (MIP) of 2.25% of the loan's value. The MIP must either be paid in cash when you get the loan or rolled into the life of the loan. Home price qualifying maximums are set by FHA.
What is negative about FHA
FHA loans are sometimes viewed as less favorable than conventional loans in a competitive market. You could end up paying more over the long term. Your interest rate may be lower, but your APR, which is the annual cost of the loan, can sometimes be higher than conventional loans.
Should I switch from FHA to conventional
It's worth it to refinance an FHA loan to a conventional loan if you've built enough equity in your home and can get rid of costly monthly mortgage insurance. However, you'll need to determine if you can meet more stringent qualifying requirements before you trade your FHA loan for a conventional mortgage.
Are FHA closing costs more than conventional
FHA loans tend to have higher closing costs than conventional loans, but because FHA loans allow the seller to pay for more of your closing costs than conventional loans, they may actually be cheaper.
What is the downside of a conventional loan
As noted above, conventional loans tend to have lower closing costs (and be cheaper in general) than government-backed options. However, the downside of conventional loans is that they don't offer as much flexibility to help you avoid paying those costs upfront.
What are the disadvantages of conventional finance
Conventional loan disadvantages
Even though the rate is great, the term won't allow you to operate your new location profitably because your monthly payments will be higher to meet the repayment schedule." "Conventional loans do not allow for projection-based financing."
Why are FHA loans less desirable
FHA financing is not trusted because real estate agents do not understand how they work. Many real estate agents think that a FHA appraisal, which is a little more thorough than a conventional appraisal, is going to jeopardize their clients sales price or identify repairs that need to be done before the sale.
What are the disadvantages of a conventional mortgage
Cons: Why a conventional mortgage may not be right for youYour credit score is below 620. The eligibility requirements for conventional loans are more stringent than government-backed loans.You have a high debt-to-income ratio (DTI).
Do FHA loans take longer to close than conventional
Some home buyers (and sellers) believe that the FHA approval and closing process takes a lot longer, due to governmental “red tape.” But that's not entirely true. For the most part, the FHA and conventional mortgage loan processes work the same way. So the timeline can be similar as well.
What is the downside to a FHA loan
FHA loans are sometimes viewed as less favorable than conventional loans in a competitive market. You could end up paying more over the long term. Your interest rate may be lower, but your APR, which is the annual cost of the loan, can sometimes be higher than conventional loans.
Why are FHA closing costs so high
Because FHA closing costs include the upfront MIP, an FHA loan can have average closing costs on the higher end of the typical 3% – 6% range. That doesn't diminish in any way the value of getting an FHA mortgage, with its low down payment, lower interest rates and flexible underwriting.
Who are conventional loans best for
A conventional loan is often better if you have good or excellent credit because your mortgage rate and private mortgage insurance (PMI) costs will go down. But an FHA loan can be perfect if your credit score is in the high 500s or low 600s. For lower-credit borrowers, FHA is often the cheaper option.
Who should use a conventional loan
If you have a credit score of 700 or higher, a debt-to-income ratio of 35% or lower, and a 20% down payment for your loan, a conventional mortgage may be your best bet. If your credit score is lower than 640 or you can't put 20% down, you may want to consider an FHA or USDA loan instead.
Is it harder to get a conventional loan
Conventional loans have to meet certain baseline requirements set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac and can be harder to qualify for than a government-backed loan.
What is the downside of FHA
FHA loans are sometimes viewed as less favorable than conventional loans in a competitive market. You could end up paying more over the long term. Your interest rate may be lower, but your APR, which is the annual cost of the loan, can sometimes be higher than conventional loans.
Why are closing costs higher on an FHA loan
Because FHA closing costs include the upfront MIP, an FHA loan can have average closing costs on the higher end of the typical 3% – 6% range. That doesn't diminish in any way the value of getting an FHA mortgage, with its low down payment, lower interest rates and flexible underwriting.
